Aicardi syndrome
Findings
• Large right paramidline fronto-parietal cyst that apparently communicates with the body of lateral ventricles and roof of third ventricle posteriorly, measures upto 8.6cm in long axis.
• Another midline extra-axial cyst in parieto-occipital region behind torcular herophili, measures upto 5cm.
• Severe dysgenesis of the corpus callosum.
• Pachygyria in right parieto-occipital region in the form of abnormal gyration, cortical thickening and deep sulcation.
• In addition, narrow closed-lip Schizencephaly in right parieto-occipital region (better appreciated on IR coronal images).
• Assymetric frontal lobes. The right frontal lobe being larger as compared to the left & shows mild extension to the left across midline.
• Tectal plate elongation.
• Deformed and underdeveloped cerebellar vermis.
• Hypoplastic falx cerebri.
• Absent cavum septum pellucidum.
• Hypoplastic superior sagittal sinus with high-riding torcular herophili and straight sinus.
• Narrow and elongated Skull – likely indicates Craniosynostosis. CT correlation is recommended.
• Mild mucosal disease in right maxillary sinus and bilateral ethmoidal air cells.
• Rest of the brain parenchyma shows normal signal and morphology. Basal ganglia, thalami and hippocampi appear normal. The visualized orbital contents and rest of the paranasal sinuses appear normal.
• Another midline extra-axial cyst in parieto-occipital region behind torcular herophili, measures upto 5cm.
• Severe dysgenesis of the corpus callosum.
• Pachygyria in right parieto-occipital region in the form of abnormal gyration, cortical thickening and deep sulcation.
• In addition, narrow closed-lip Schizencephaly in right parieto-occipital region (better appreciated on IR coronal images).
• Assymetric frontal lobes. The right frontal lobe being larger as compared to the left & shows mild extension to the left across midline.
• Tectal plate elongation.
• Deformed and underdeveloped cerebellar vermis.
• Hypoplastic falx cerebri.
• Absent cavum septum pellucidum.
• Hypoplastic superior sagittal sinus with high-riding torcular herophili and straight sinus.
• Narrow and elongated Skull – likely indicates Craniosynostosis. CT correlation is recommended.
• Mild mucosal disease in right maxillary sinus and bilateral ethmoidal air cells.
• Rest of the brain parenchyma shows normal signal and morphology. Basal ganglia, thalami and hippocampi appear normal. The visualized orbital contents and rest of the paranasal sinuses appear normal.
Diagnosis
Aicardi syndrome
Teleradiologyhub FRCR , MD , DNB , MNAMS is a Assistant Professor from with experience of 11-15 years post-graduated from Tata Hospital, Parel. Specialized in Reporting of CT-SCAN , MRI cases with expertise in Neuro-imaging , Spine-imaging , Musculoskeletal , Stroke-imaging
Are you looking for Paid consultation or Second Opinion from Expert Radiologist ?
Consult Teleradiologyhub
Page Visits : 138

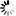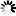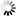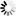 Loading
Loading